Understanding 1e100.net in Google's Email Forwarding System and DMARC Reports
Organizations must implement email security and authentication to protect against spoofing, phishing, and other threats. The role of forwarding systems and their interaction with email authentication protocols like SPF and DKIM are critical yet often overlooked aspects of email infrastructure. DMARC reports frequently feature Google's 1e100.net domain, raising concerns among domain owners and IT professionals. This article will explore the significance of 1e100.net in email forwarding, its implications for DMARC reporting, and the challenges it poses for DKIM and SPF. Additionally, we will provide practical solutions and best practices to address these issues, ensuring the security and reliability of email communications within your organization.
What is 1e100.net?
Google owns the domain 1e100.net, which frequently shows up in DMARC reports under the Gmail Forwarding email server. It is a representation of Google's email routing and delivery infrastructure. This domain is used by Google services, like Gmail and Google Workspace, to identify and reroute emails sent from their servers.
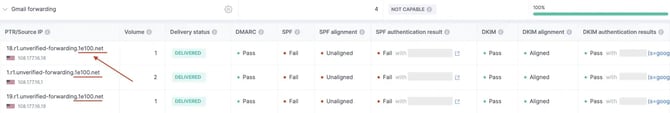
1e100.net's Connection to Email Forwarding
A DMARC report that has a 1e100.net address in its SMTP trace is one that is being delivered via the Google network. Unverified forwarding setups for mail are routed through Google servers with public IP addresses via Gmail. The public IP addresses resolve to Google hostnames that end in unverified-forwarding.1e100.net and are purposefully omitted from Google's SPF record. These servers route communications that are not validated using the IP address ranges listed in this article.
DKIM and SPF Issues with Email Forwarding
SPF Challenges:
In the context of email forwarding, SPF frequently fails due to misalignment. This fails because the return-path address domain will be different from the mail-from address domain.
As we address below, emails forwarded over 1e100.net and Google Groups may also fail SPF authentication since the Return-Path domain does not always contain 1e100's IP addresses under its SPF record.

The drawbacks and advantages of DKIM:
One of the key advantages of DKIM over SPF in the context of forwarding is that DKIM can survive the forwarding process, provided the email content and relevant headers remain unchanged. This means that even if an email passes through multiple servers, as long as the DKIM signature is intact, the email can be authenticated as originating from the claimed domain. However, any modifications to the email content and the header, such as adding footers or banners, can invalidate the DKIM signature.

Handling 1e100.net in DMARC Analysis
When analyzing DMARC reports, encountering 1e100.net can indicate that emails have passed through Google's infrastructure, often due to forwarding via Google Groups. To mitigate DMARC failure issues, it is crucial to ensure that your email servers are correctly configured, especially for DKIM. Proper DKIM setup ensures that the cryptographic signatures remain intact, allowing the forwarded email to be authenticated successfully despite SPF failures.
For a detailed, step-by-step guide on how to configure DKIM for Google, please refer to the following link:
DKIM Setup for Google Workspace
We also provide guidance on setting up SPF and DKIM for hundreds of other Email Service Providers (ESPs). Be sure to explore our database to verify that your DKIM configuration is accurate and effective.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the role of 1e100.net in email forwarding is key to accurate DMARC analysis. While SPF failures are common due to the nature of forwarding, DKIM signatures can provide reliable authentication if properly configured. Organizations, particularly those using Google Groups, should ensure their SPF and DKIM settings are correctly established to maintain secure and authenticated email communication. Properly setting up these protocols will help in achieving consistent DMARC compliance and protecting against potential email spoofing and phishing attacks.