The Role of ARC (Authenticated Received Chain) in Email Forwarding
ARC (Authenticated Received Chain) is an email authentication system designed to validate an email's journey from its origin to the final recipient, preserving authentication results even when emails pass through intermediaries (such as auto-forwarding services).
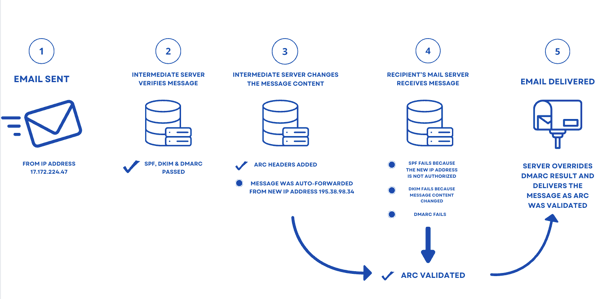
Mailing Lists, Auto-Forwarding, and ARC
When emails pass through intermediate mail servers like mailing lists or auto-forwarding services, SPF often fails because the original sending IP address is lost. In such cases, DKIM can still help by ensuring the authenticity of the email's content, regardless of the sending IP.
However, in certain situations, the email's content or headers may be altered during the transition through multiple servers. This could cause both SPF and DKIM to fail, resulting in the email failing DMARC checks as well.
Given the challenges associated with SPF and DKIM failures when emails go through intermediaries, ARC plays a crucial role. ARC is especially useful when legitimate emails fail DMARC checks after passing through multiple hops or intermediaries. Although SPF and DKIM may fail due to header changes or IP address modifications, ARC preserves the authentication results throughout the email's journey. This enables the final recipient's mail server to verify that the email is legitimate, even if the original SPF or DKIM checks would have failed.